How to choose inline skates

If you want skating to bring your joy it is necessary to choose skates properly. It is not so easy, but neither is it science, however many customers make mistakes. Then how to choose skates?
It is crucial to realise what kind of skating discipline you want to do. According to this you have to choose certain type of skates. Further information are: zde.
We are going to focus more on fitness category in this article, because it is the most common. They are suitable for recreational, fitness and sport skating on cycle tracks. We will also go through tome technical details of particural parts.

Caution! All information about individual parts stated below are only indicative. Always depends on whole construction of skate. Quality of certain part does not guarantee good skating quality. The best skates are well constructed as a hole which consist of many high-quiality components.
The most important factors for the right choice:
1. Size and amount of wheels: affects mainly speed, stability and nimblenes.
2. Length of fram - nimbleness, directly proportional to wheel size
3. Quality/toughness of the boot - stability, transfer of energy to rebound, comfort
4. Rigt size - stability, nimbleness, comfort
Other important aspects:
1. Wheel quality and hardness
2. Quality of bearings
3. Frame firmness
Consider also these details:
1. Frame attachement/possibility of adjustment
2. Lacing system/ buckles
3. Focus point
4. Ventilation
5. Weight of skate
6. Chimney/ front-back flex
7. Availability of spare parts
8. Details (material and quality of screws, sewing, type of brake, spacers etc.)
Wheels
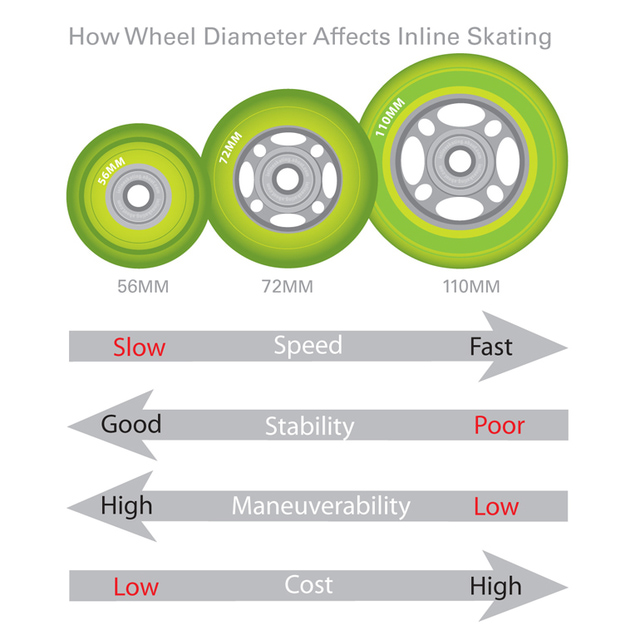
Size of wheels
General:
Bigger wheels = higher speed, longer frame, higher focus point > worse stability and nimbleness
Smaller wheels = lower speed, shorter frame, lower focus point > better stability and nimbleness
With adult fitness skates are used wheels in these sizes:
less than 80mm - nowadays, wheels smaller than 80mm are used very occasionally. Smaller wheels are used with older types of skates, special types (freestyle, inline hockey), kids skates and singularly with fitness skates for beginners.
80 mm - the basic fitness skates. Nowadays the less used type. Suitable for beginners and recreational skaters. Usually with bearings ABEC/ILQ/SG 5.
84 mm - suitable for beginners or mid-level experienced skaters who search for nimble skates. Usuaully with bearings ABEC/ILQ/SG 7.
90 mm - top inline skates. Suitable for experienced skaters who like faster ride. Usually with bearings ABEC/ILQ/ SG 9.
100 mm - fast and not much nimble skates suitable for fast ride and long tracks for experienced skaters. Usually with bearings ABEC/ILQ/ SG 9
110 mm - fast and not much nimble skates suitable for fast ride and long tracks for experienced skaters with excellent skating technique. Used usually for speed and semi-race skates.
125 mm (always frame with 3 wheels) - nowadays the biggest wheels used in fitness and race field. They are used always as 3 wheel skates. Advantage is good ratio of speed and nimbleness. Disadvantage are worsen acceleration and higher focus point.
Amount of wheels
2 wheels- used with special models such as nordic skates (inflatable wheels), skate ski or aggressive skates.
3 wheels- very popular lately. Good ratio of speed to nimbleness. This allows to use bigger wheels but maintain short and nimble frame. Simultaneously this allowed to increas the size of sped skates for 125mm ( 4 x 125 mm would mean too long frame). 3 wheels are also used with kids skates to cut down the weight and to shorten the frame.
4 wheels- the most common amount of wheels. Providing good ratio of speed, adhesion, nimbleness. Used with all types of inline skates. Maximum size is currently 4 x 110 mm.
5 wheels- 5 wheels are used with older types of speed skates, downhill skates and alpine slalom.






Quality and hardness
Basic types of wheels according to type:
Fitness wheels
Freestyle/freeskate wheels
Aggressive wheels
Speed wheels (speedskating)
In-line hockey wheels
Trekking wheels (Squad)
Nordic wheels (inflatable or PU)
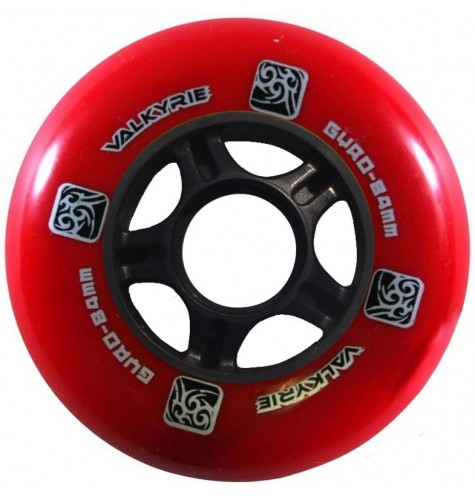







The most important features:
Material of wheels
Hardness of wheels
Further information:
wheel profile
weight
center of wheels

Material
Basic material is polyurethan (PU). Quality is determined by additives. Final material affects quiality of ride and also the price.
The cheapest wheels are made of PVC, we definitely do not recommend either sell these wheels, because they are not suitable for skating.
Top level wheels are made of dual mixture. Inner part is made of softer PU which provides better adhesion and rebound. Cover part is made of harder PU which provides longevity and smoothness.
Special PU mixture is for wheels intended to rainy days. This mixture provides great adhesion even on wet surface. Price is rather high and they are used mainly for racing.
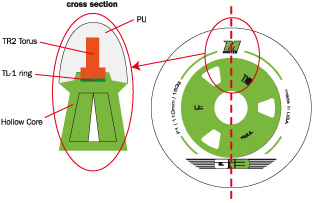


PU quality determines:
adhesion (grip)
smoothness (resinstance > speed)
absorbind
longevity
Hardness of wheels
General:
Harder wheel = higher speed, less wore out, worse adhesion, worse absorbing
Softer wheel = lower speed, higher wore out, better adhesion, better absorbing
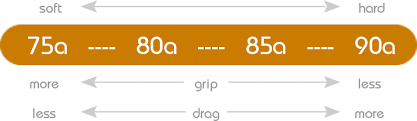

Hardness marking:
a) the most common way of marking is number and letter A (for instance: 82 A) - measureing is done with durometer, letter A marks unit of measurement and actual hardness is measured. Fitness skates are usually within the range 80 - 87 A. The higher the number, the harder the wheel (and suitable for faster ride)
b) less usual way of marking is number F and numbe 0-3 (for instance: F 3). This footprint scale was invented because use of durometer does not reveal all atributes important for hardness. The higher the number, the softer the wheel (F0 = the hardnest, F3= the softes). It is specific marking used by certain producers. At the same time, it is way of marking actual wheel collection - F1 wheels for circuit are different than F1 wheels for asphalt.
Hardness also differes in type of use. There are special soft wheels for artificial surfaces (inline hockey, speedskating) or on the contrary extremely hard wheels for aggressive skating.
Conversion (durometer > footprint):
F0 = 88A
F1 = 86A
F2 = 84A
F3 = 82A
Caution! Information about hardness are not exact. It always depends on actual quiality of wheels. Significantly more expensive wheel can be far more better even though the marking is the same as with cheaper wheel. It can happen, that expensive wheel with high-quiality additives with hardness 86 A will have better propreties than cheaper 84 A wheel.

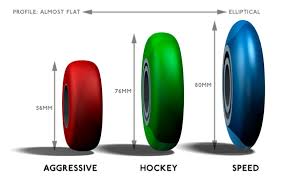
Wheel profile
You can also notice differences in profiles of wheels. Profile of wheels usually differes in certain skating discipline they are used for. Usually, the differences are not particulary noticeable during ride.
General:
wide profile = better stability and adhesion, lower speed. Suitable for freestyle and aggressive skates.
narrow profile = higher speed (due to lower friction). Suitable for fitness and racing skates.
Weight
Weight is a matter of question usually when it comes to speed skating, semi-race skates for long track and models with emphasis on the lowest possible weight. Description of racing wheels usualy includes amount og grams, but seight of common fitness wheels is hardly ever stated.
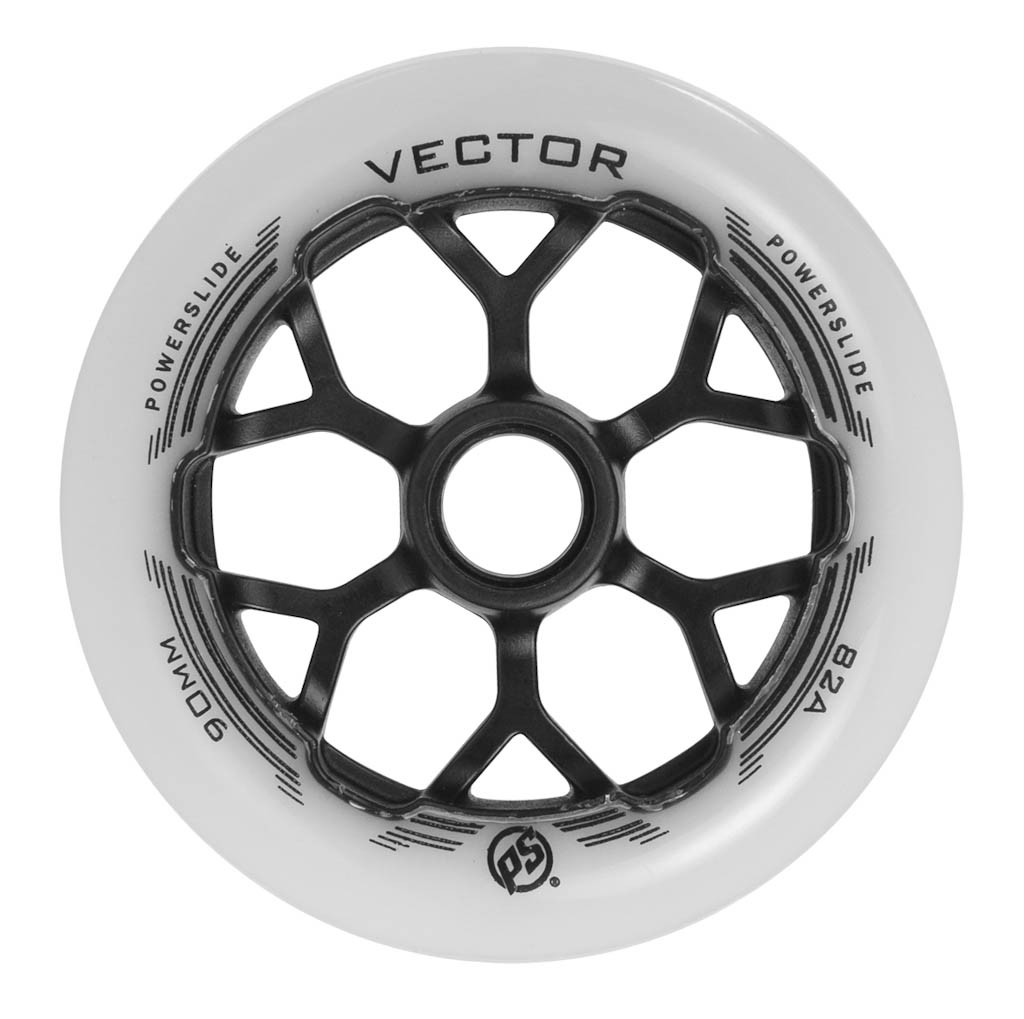


Midpoint of wheels
Midpoint of wheels affects mainly weight, hardness and rebound. Racing skates need better constructed midpoint for better adhesion and rebound. Freeskates have usually full midpoint in order to maintain resistance during jumps and tricks. Fitness skaters usually do not care about midpoints, effects on ride are usually hardly noticeable.


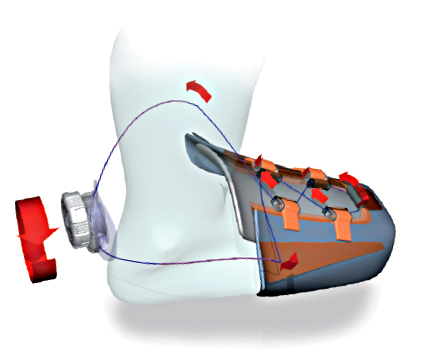
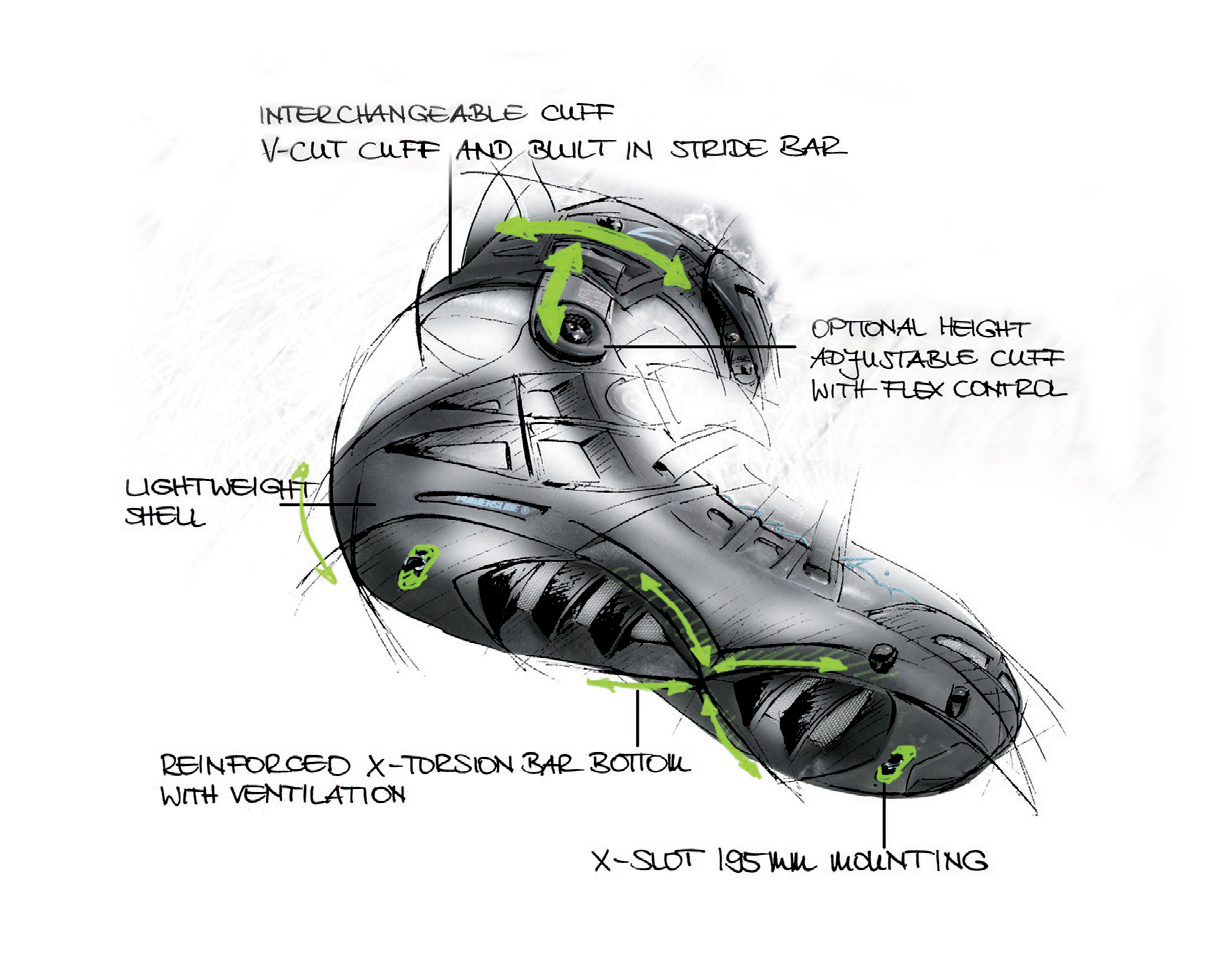
Frame
Length
Length of frame affects nimbleness of skates, slide and stability during moments of higher speed. Length of frame is directly proportional to size of wheels. The bigger the wheels, the longer the frame. Length of frame is expressed usually in inches or centimeters.
Shorter frame - better controllability, worse stability during moments of higher speed

Longer frame - worse controlability, better track lead, better stability during moments of higher speed
Recommendations are not exact, even with shorter frame it is possible to skate fast. Important aspects are also firmness, focus point, toughness of boot etc.
Toughness of frame
Toughness affects mainly stability of skate (especially during faster ride), tranfer energy to rebound and resistance. It is determined by used material, way of attachment and technical manufacturing.materiálem, způsobem
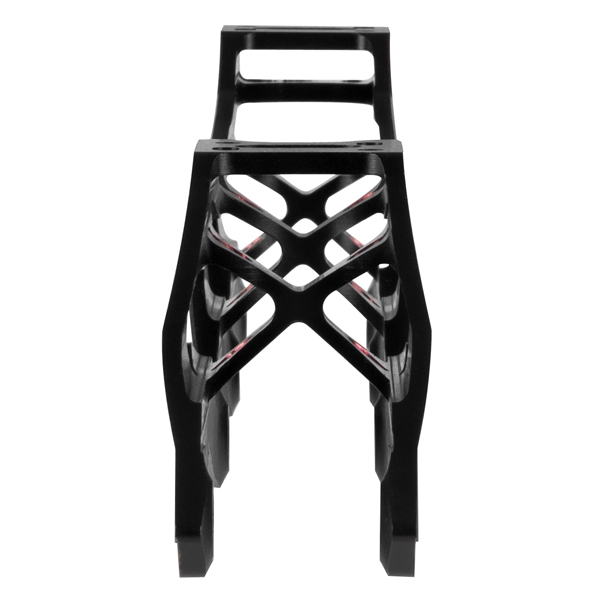

Construction - the aim is to achieve optimal ratio of (high) tougness to (low) weight. Frame has to also be felxible. High-quiality frames are made of CNC milling machines which provides precise manufaturing. They are however quite expensive. Higher toughness is maintain using bridges (braces in frame construction).
Toughness is higher with mono-constructional (=made of one piece in shape of U - always attached with screws), compared to traditional frames which are made of two pieces integrated to bottom part of the boot (usually rivetted). However, it always depends on type.
Materials
a) Plastic frame - plastic frame is used usually with fitness skates for beginners or with aggressive (harder version). Advantages are low price, weight, good absorbing of bumps. Disadvantage is low level of toughness.
Plastic frames differs in quality a lot. Expensive plastic frame could be better than cheaper metal frame.

b) Metal frame - usually it is made of aluminium alloy. Alloy affects price and quality. Cheaper frames are made of softer and cheaper metals, top frames are made of expensive and more solid materials such as Aircraft aluminium (aluminium alloy used in aviation industry), alloy Al 7005 (93,35%Al, 0,13%Cr, 1,4%Mg, 0,45%Mn, 0,03%Ti, 4,5%Zn, 0,14%Zr) etc. Metal frame does not guarantee quality, you have to always consider all features.
![]()
Magnesium - low weight, but fragile and lower bearing capacity
c) Carbon frame - carbon frames are used only with top level speedskates and freeskates. Advantage is mainly low weight, therefore these frames are used for sprints. Disadvantages are higher price, lower toughness (compared to the best metal frames offered).

Ways of attachement and possibility of frame adjusting
Types:
rivetted frame - frame taht consist of two parts. Attached with rivets or screw right to the bottom part of the shell. Advantage is low weight. Disadvantages are lower toughness and no possibility of adjusting frame position.

screwed frame- usually used with fitness, race, aggressive and freestyle skates, when there is emphasis on toughness. We can also find them with cehaper skates, but usually with low-quiality frame. Advantage is also possibility of adjusting the frame position. Screwed frames are mono-constructed (made of one piece in shape of U) and they are attached through the holes to the boot where the thread is (see picture 2).





Spacing of screwed frame
150 mm - used with kids racing skates
165 mm - used with skates with smaller wheels (max. 84mm), with 3-wheel-skates, freeskates and smaller sizes
195 mm - used with bigger wheels (over 90mm) + bigger sizes
UFS - standardized attachement of aggressive skates
Some frames have two slots for better attachement of spacings
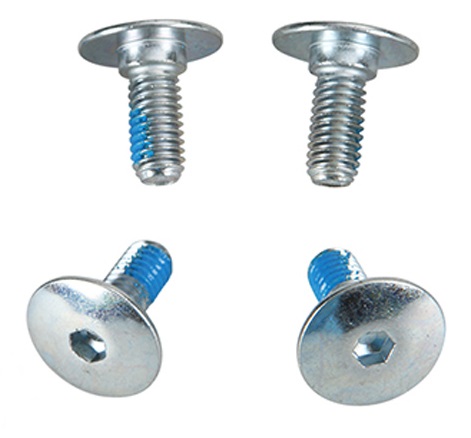





There are sometimes other spacing. Usually it is matter of certain fitness type of skates. However, it is not a standard spacing.


Frame adjusting
Adjusting position of the frame is done for adjusting the frame to boot. Usualy is possibility od front-back and side adjustment. At the same time, angle of the frame can be adjusted using special gores. Setting depends on certain needs of skater (according to its foot and individual preferences). There has to be longitudinal (along) and tranverse (across) slot for screw (otherwise it is not possible to adjust it). Frame slots have to be croswise to each other.


Front-back setting - used mainly for racing skates. Advantage is possibility of exact setting of focus point (= exact rebound). If the frame is too forward, the rebound is done on front wheels through the tip, which is the most common mistake. If the frame is too backwards, it can lead to problems with instep tendon and shin muscles.
Side setting - for exact focus point and precise feet axis. This is very individual and it can really help to prevent from pain. Correct setting can also affect stability during slide.
The most common setting of frame is that the middle of back wheel is set in direciton of achilles tendon. Front position (=front wheel) is usually under the second finger.
Centering with gores
gores can be used with certain types of racing frames. Gores are placed as a pad between the frame and the boot. Gores are called Pitch control and Stride control. Front-back and side lean can be adjusted with gore.



Pitch control - enables change of front-back angle. The heel is either adjusted higher than the tip or other way round. First option provides better acceleration. This setting can be seen in sprint disciplines and short tracks. Suitable for everybody who preferes good acceleration. Second option (the tip is higher) is used for long tracks during which is skater often in vertical position and weight is put on the middle of the frame and back wheels.
Stride control -enables change of side angle. Frame is then more to the left or to the right. Advantage are longer slide and powerful rebound.



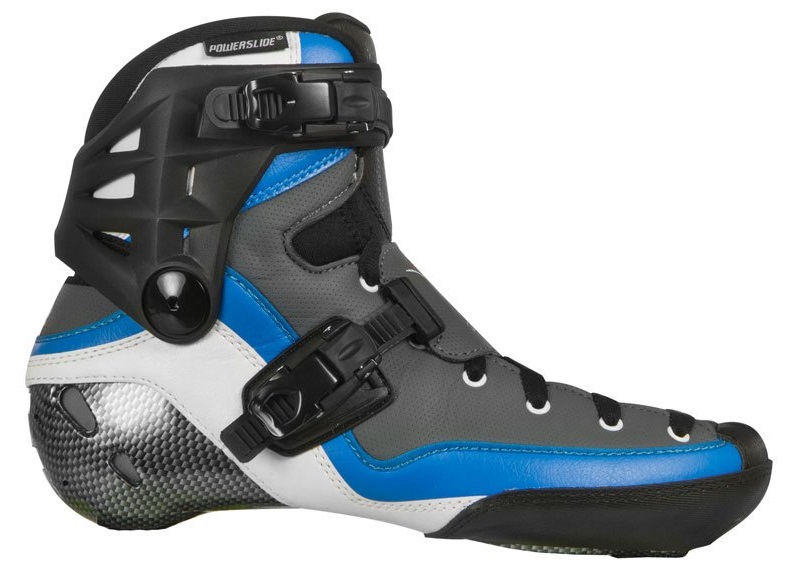
Boot
Toughness
Toughness of the boot is important and most underestimated factor. It affects stability, comfort and controllability of skates. Sport skates have always firmer boot and other way round - recreational skates have usually soft boot.
Generally:
Tougher boot = better stability, controllability, transfer of energy, lower comfort
Softer boot = worse stability, controllability, transfer of enerfy, higher comfort, better ventilation




Correct size choice
It is very important to choose the right size of skates.
Boot which is too small could cause sores, blisters, arch pain, foot pain etc. In this shoe you will not love skating very much and be looking forward to putting them of. On the contrary, bigger boot does not bring required support, especially on the sides and during energy transfer. Skaters has no support and will ´´pigeon toed´´ in such skates. Also is not real to do a proper rebound and slize in skates that are too big in sizing.
Information about sizes are here

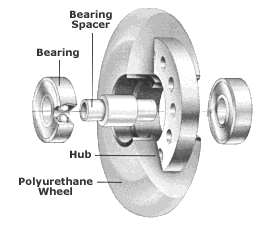
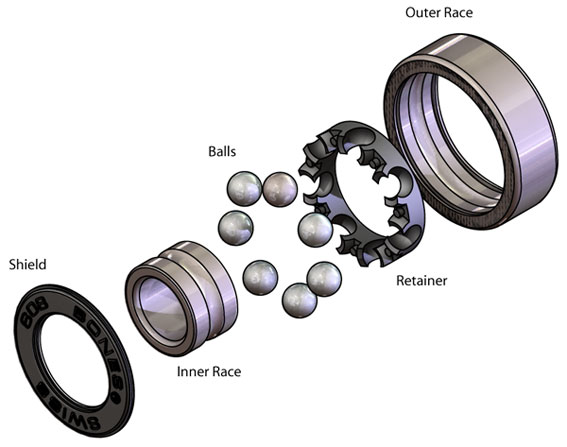
Bearings
Bearings affects speed and comfort of ride due to spinning.
Size of bearings
there are two standardized size of bearings:
608 (basic size) - the most common size used, 90% of skates
688 (micro bearings) - not usual, used mainly for lower weight. Disadvantage is shorter longevity. It must be used with wheels especially made for this bearings.

Spacers
Spacers are used for exact positioning of bearings. When you don´t have precise spacer, bearings get stuck after tightening and they spin worse. To smoothness of bearings are spacer very important. There are generally two lengths of spacers:
Spacer 6.2 mm - spacer in shape od tube going through the middle of bearings. Makes the centre of bearing thinner (aprox. 6mm). They are used with screw with counterparts, mainly with fitness skates (typical for K2 skates). These thinner spacers are offered in shorter versions with distant pads which are places between the frame and the boot. Used usually with cheaper or older models.
Spacer 8 mm (wider) - standard size for majority of skates. It mach with center of bearing, screw goes through the bearing and spacer is placed between the bearings. For exact centering there are various diameters (10.31 mm,10.35 mm etc.).
Spacery for microbearings 688 (6 or8 mm) - specific smaller spacers for smaller microbearings. They are also divided according to inner diameter to 6.2 a 8 mm



Quality of bearings
The most important factors are:
Material
Accuracy and quality of manufacturing
Type of greasing
Type of covering
Producers
Other factors can be:
ammount of balls in bearing
material of balls cage
weight
marking (ABEC, ILQ, SG, HTO etc.)
Material of beraing
Basic division:
carbon steel - lowe-quality, chaper skates
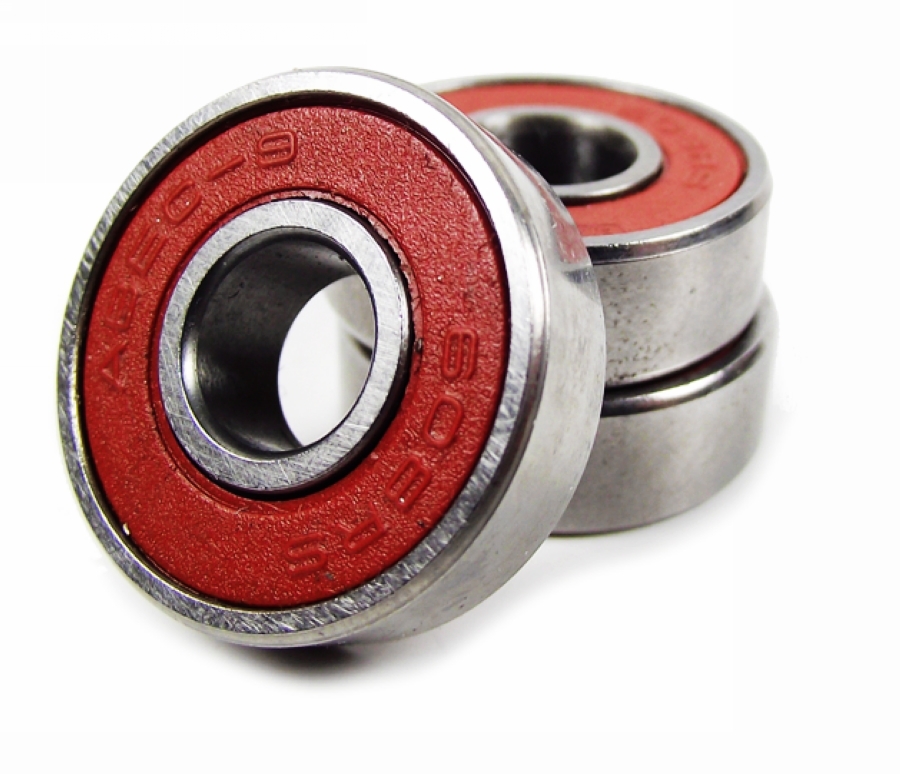
chrome steel - the most common metarial. Quality is determined by quality of steel which affects total price and overall qualit of bearing
stainless steel (anticorrosion semi-ceramic and ceramic bearings) - suitable for rainy and wet weather
titan bearings - used for aggressive and freestyle skates. Less used type.
Semi-ceramic bearings - the most expensive type of bearings used for racing and speed skating. Advantage is that when metal rings touch ceramic balls there is lower fricton and therefore better spinning od bearings. Ceramic balls are also lighweight, harder and usually are combined with stainless steel. They can be then used in rainy or wet weather.
Materials of semi-ceramic bearings:
a) Oxide Zircone (ZrO2) white ceramic - longevity of bearings made of this material is 2x - 3x higher than usual metal balls. At the same time, they are harder thatn black ceramic balls. Disadvantge is that they need to be greased precise.
b) Nitride Silicon (Si3N4) black ceramic - nitride silicon is 40% lighter than steel. Extremely low roughness provides longevity and eliminates friction. These bearings don´t need to be greased regularly, they can be used dry after first greasing - but this increases the risk of damage.
Full-ceramic bearings - less usual type are full-ceramic bearings. They are very expensive, hig-quality ones are more expensive than fitness skates. In race skating there are mainly semi-ceramic bearings used.





Quality of manufacturing
Precision and technical quality are important factors. They are given by honesty and output checking of each producer. For precision is used technical standard ABEC, however it does not define quality of bearing. Further information can be found in Marking bearings (ABEC, ILQ, SG, HTO etc.)

Greasing
All greases are based on basic friction theory and its effects on material.
Greasin affects speed, resistance against dirt, requency of refilling, and longevity. We use:
Oil- provides the least friction due to lower density. The output is high speed but lower resistance against dirt and frequent need of refilling. Oils differ in density and composition. Bearings greased with oil are used with racing skates, beacuse it is expected that they are serviced regularly.
Vaseline (fat) - significantly enhances resistance against dirt and prolnged grequency of refilling. Bearings greased with vaseline have to be ´´entered´´, you have to skate for some time to gain required speed. Vaslina is used with recreational skates which don´t demand so much service.
Gel - its atrributes is it something between oil and vaselina. It has higher density compared to oil (therefore it protect against dirt better), but it can still provide higher speed.
Caution! Type of grease affect wheel spin. Bearings with vaseline will have shorter and lower spin, compared to the same bearings greased with oil. It is not true then, that we can guess quality from bearings spin.



Viscosity- express slipperines of greasing. The lower the viscosity, the lower the fricition. This means better spinning of bearing. Viscosity also affects adhesion of bearings and determines longevity of greas. Vaseline has higher viscosity (compared to oil), last longer, but the bearing is a bit slower (due to higher friction).
Ceramic particles in grease - eliminates the temperature during the friction, enhances longevity and quality during highe speed.
Cleaning- if you want to take care of your bearings, you have to celan and oil your bearings regularly. Not all bearings can be serviced though. Possibility of cleaning is given by way of covering. Remember that vaseline is hard to clean and it is harder to get rid of it.
Maintenance-free bearings - bearing heavily greased with vaseline and usually there is not possibility of removing the cover. It doesn´t mean that the bearings have unlimitied longevity, they are only more resistant against dirt and could last longer without any maintanance. Even these bearings can rust after rain or get dirty. Keep also in mind, that these type of bearings are usually slower (dense vaseline increase the friction - lower speed). On the contrary, racing berings have always removable covers to enable regular service and cleaning,
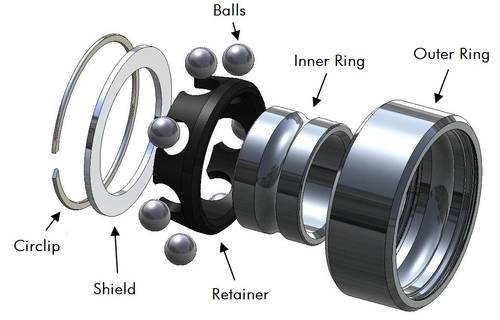
Type of covers (gasket)
cover keep lube inside the bearing and prevent from dust and dirt.
Basic division:
Contactless bearings (mark with letter Z) - cover doesn´t touch with inner bearing ring which provides higher speed and lower friction. Covering is always metal. Disadvantages is worse resistance against dust, rust, lube leak. Advantage is higher speed. 
Contact bearings (mark with letter S) - cover touches inner bearing ring. Disadvantage is higher friction adn lower speed. Advantage is better resistance against crashes and dirt. Contact bearings are suitable for those who prefer longevity and minimal maintenance.
Basic marking of bearings accordint to type of cover:
Z - one metal cover
ZZ - two metal covers
Metal covers can be right on the bearing so it is not possible to remove it. Bearings cannot be cleaned and oiled (for instance: Rollerblade SG or cheaper models with ABEC bearings). Second option is removable cover. Bearings can be cleaned and oiled (for instance: some types of ILQ or high-quality ABEC - BSB)
S - contact bearings (inner cover touches the ring)
R (rubber) - bearings with rubber cover
RS - contact bearings with rubber cover
SCRS - special rubber contact gasket providing better resistance against dirt
Rubber cover can be always removed using a pin. You just scoop the gasket (where the ring is smaller) and move pryly and rotarly to uncover it.



Producer
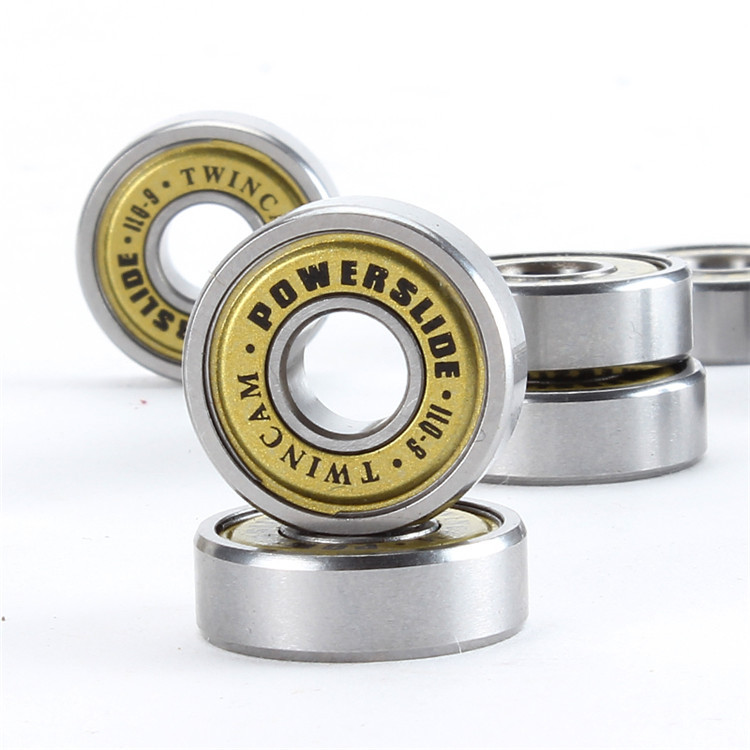
In case you don´t want to understand details of bearing, the basic precondition for choice is producer and price. Usually it is really the true, that proven producer offers high-quality bearings no matter how it is marked. On the contrary, bearings from unknown producer without previous experience with that type of bearings is very risky. No matter wheter it is marked as ABEC 5 or ABEC 9. Also it is true that bearings that cost 1000 CZK are better thatn those that cost 500 CZK and again, no matter the marks and labels are. The most famous producers of bearings are for example Twincam (ILQ bearings), BSB , Kryptonics, SKF, FAG, Labeda and many other. Sometimes certain producers offer bearings made by big supranational factories. You can therefore buy ILQ bearings from Twincam from K2 or Tempish. Or for example FAG produces bearings for german Powerslide etc.






Number of balls
The amount of balls in bearings is usually 7. But for examle Twincam has 6 balls. It can also differ in size of the ring and its weight. It is more like constructing attribute, amount of balls doesn´t itself affect quality of the bearing.
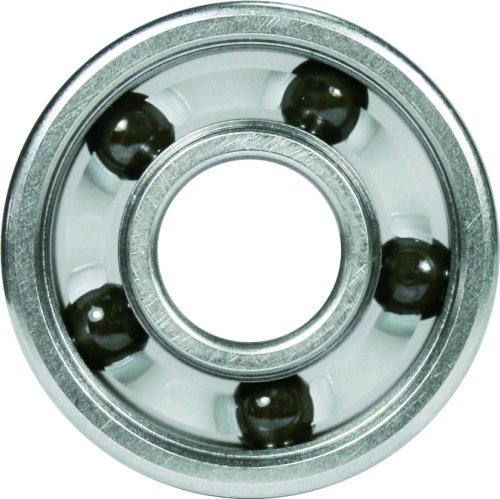


Cage
Helps to keep balls in correct distance from each other - prevents from their contact and therefore lowers the friciton. Also provides even distribution of weight.
Basic division:
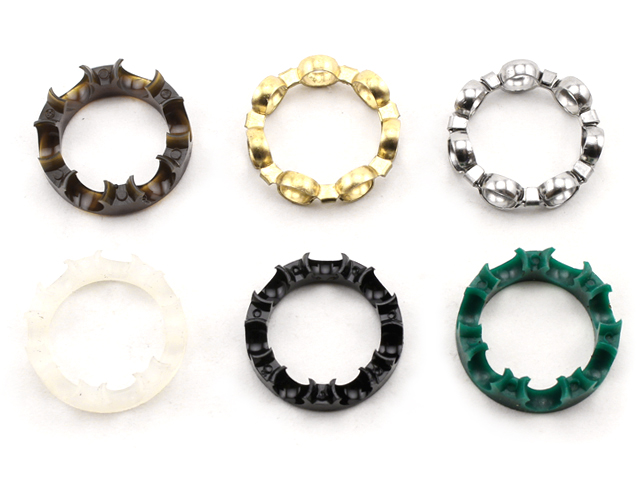
polymer cage - provides good slipperiness on metal areas and smooth surfaces. Contributes to low friction, temperature and wear and tear. Also provides good spin even with insuffucient greasing without seizure. The price is higher so it is used with speed bearings. Polymer cage can be removed in order to offer precise but also more demanding maintenance.
metal cage - it has universal use and friendly price - suitable for common recreational or fitness bearings and skates. Along with usual chrom steel it can be made of coal steel, brass etc. Bearings with metal cage have to be always lube well to prevent seizure.

Weight of bearing
Mostly racers and long-track enthusiast put emphasis on the wegith of bearing. Common skater doesn´t feel the difference. Weight is determined by construction and material.
In general, semi-ceramic bearings, micro 688 bearings or bearings with less balls or with special thinner rings are lightweght.

Marking ( ABEC, SG, ILQ, HTO etc.)
1. Technical standard of accuracy ABEC - ABEC is abbereviation for Annular Bearing Engineering Committee. This standard states precisely what deflection is permissible for the bearing to be marked with ABEC. The higher the number, the more accurate the bearing. For skates the scale is ABEC 2, 3, 5, 7 and 9.

Caution! ABEC does not state the quality of the bearing! The reason is that ABEC mark doesn´t include metarial, greasig, cage, amount of ball, type of cover etc. At the same time, there is no output chceck guaranteed in order to verify ABEC mark. In practice it is usual that you can find cheap ABEC 9 bearings with low-quality or expensive ABEC 5 with excellent quality. Therefore, only bearings from the same producer and from the same collection can be compared. It is true then, that BSB ABEC 9 are better than BSB ABEC 3. But it is worthless to compare Tempish ABEC 5 and Powerslide 7 because the quality cannot be discover (using these factors).
Swiss - you can also sometimes see the mark swiss (swiss original, swiss lite, swiss (WIB). They are bearings designed (swiss lite) or made (swiss original) in Switzerland. These bearings eceed the ABEC standard. But also it is matter of quality and manufacturing. You can buy Swiss lite bearings from Chine that cost 1300 CZK or swiss original WIB that cost 4000 CZK. Quality is very different then.

Rustproof - stainless metal covers suitable for rain. Producers are for examle Twincam or Powerslide. There are always two rubber cover (RS, SCRS) and vaseline is dense.

2. Certain producer´s way of marking - ABEC standard doesn´t imply the quality of bearing, some producers use their own marking in order to specify what the quality of bearing is.
a) ILQ (Twincam USA) - bearings ILQ from american concern who also produces bearings for motorbikes, ships etc. Section for skate bearings was founded in Japan and it is called ILQ. Various skate producers buy these ILQ bearings such as K2, Powerslide or Tempish.
The higher the number, the better and more expensive the bearing. Majority of ILQ Twincam bearings has only 6 balls (compared to usual 7 balls). Except ILQ - X MR2 - this have 7 balls.
ILQ 5 - basic type, less used. Removable covers (ZZ). Metal cage. Vaseline. 
ILQ7 - used with intermediate and upper skates. Removable covers (ZZ). Vaseline.
ILQ 9 Classic - for high-quality fitness skates. Removable covers from one side, the other is open for easier greasing and lower friction. Polymer cage. Vasline.
ILQ 9 Classic Plus - for high-quality fitness skates. Removable covers from one side, the other is open for easier greasing and lower friction. Polymer cage. Vasline.
ILQ 9 Pro - for sport and some racing skates. Better resistance against dirt and oil leak due to rubber cover. Rubber cover only from one side, the other is open for easier greasing and lower friction. Gel.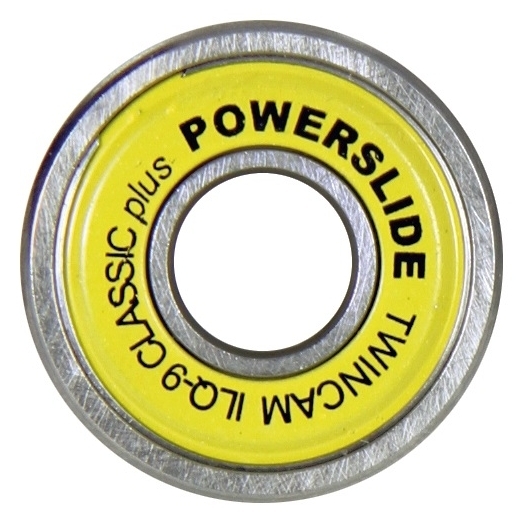
ILQ -X MR2 - for speed skates. Suitable for higher speed and decreasing the overal weight. Inner ring is wider than usual bearings 608 and balls are smaller. Compared to other ILQ types there are 7 balls. Their weight is also 29% lower than usual 608 bearings. Standard inner diameter is provide by distant pad. Rubber cover is from one side, other is open for easier greasing and lower friction. Gel.
Twincam produces other types of bearings. For instance semi-ceramic (BCB) or stainless metal bearings for rainy days (Twincam Rustproof). However, these types are not quite common.
b) SG, HTO (Rollerblade) - marking used by american company Rollerblade. You find only this way of marking - the reason is to differ from other producers and from ABEC standard which is not so reliable.

SG 3 - kids skates. Without removable covering. Dense vaseline.
SG 5 - basic types of skats for beginner. Without removable covering. Dense vaseline.
SG 7 - fitness and freestyle skats. Without removable covering. Dense vaseline.
SG 9 - top fitness and freestyle skates, basic types of speedskates.
HTO Racing - racing/speed skates. Removable metal cover from outer side and removable plastic cover from inner side. Polymer cage. Vaseline.


c) other - there are many bearings with specific marking such as Tempish Hi-Speed TRT 11 or Bones Super Reds. It defines certain quality of bearing type. In these cases we recommend to follow your experience, reviews, recommendations or price.

Other propreties and details
Lacing system and buckle
Traditonal laces - the most common way of lacing. Advantage is possibility of precise tightening in certain place and accroding to shape of the feet (more tightened tip). Speed and racing skates have usually was laced providing better fixation because they don´t come loose.
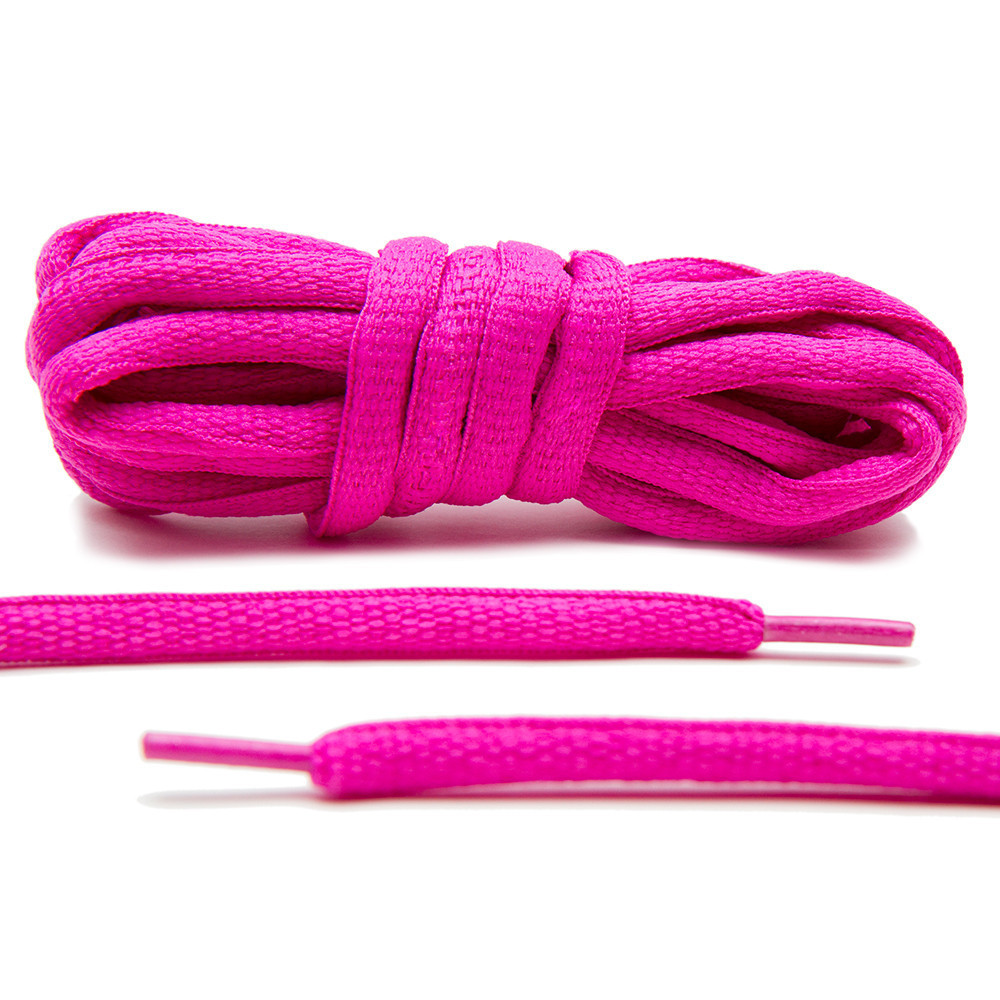



Speed laces - lace which goes through the zipper and the ends are combined together above the zipper and form a simple hold. Advantage is faster lacing. You just pull the connected ends of the laces, shift the zipper down and the skate is tightened. From personal experience we can say that for better fixation is good to first tighten the lace in the tip and then use the zipper. Loosening is done by integrated safety lock.


String fast lacing systems (K2 Boa, Powerslide ATOP, Fila Q-Fit etc.) - Lacing is done with fast system with steel or nylon string. By rotating the wheel the string is tightened which provides even and reliable fastening and fix leg in the skate well. Loosening is done by pulling the wheel forward (K2 Boa) or rotating the opposite direction (Powerslide, Fila). Advantage is fast, easy and even tigtening which doesn´t require much strength, quite easy possibility of tightening during ride and fast way of loosening. Disadvantage are higher price, higher risk of damage and also ven tightening may someone found inappropriate. There other fast lacing systems such as Rollerblade (old types) which used pulley for lacing, but this system is not used today anymore.

Buckles - old and kids skates. These way of tightening is not usual nowadays because it is not so accurate, even and reliable.

Velcro - ocasionally (K2 The Don, Powerslide PH Reign II etc.)


Buckle manufacturing
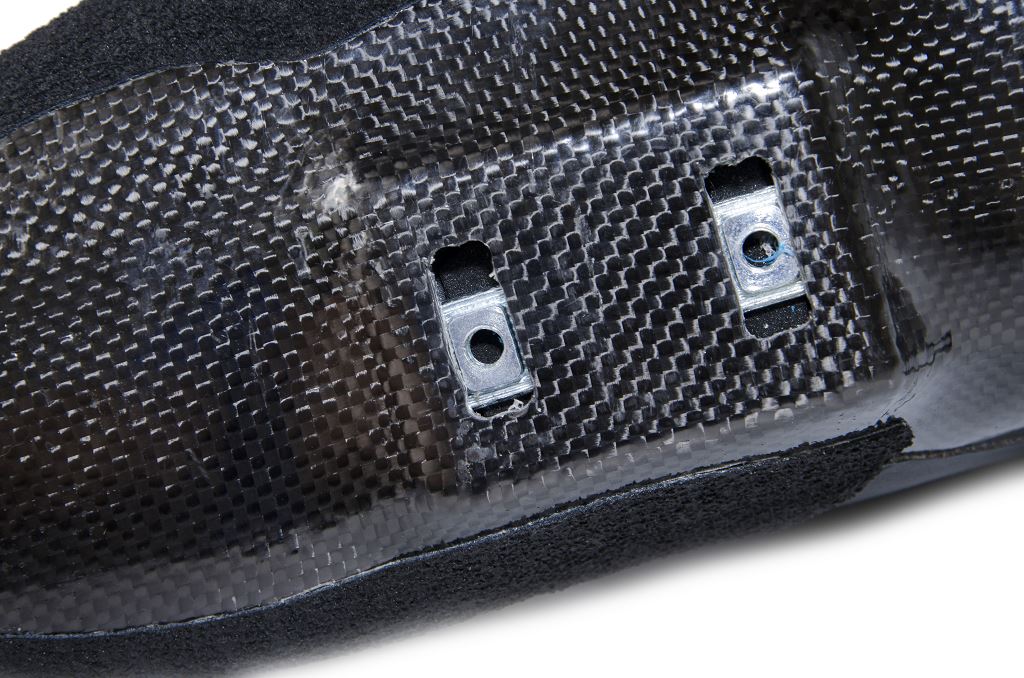
Buckles can be used for tightening the skat above the ankle (usually plastic), over the instep it is velcro, sometimes in area of tip (velcro). Plastic buckles can be attached with screws or rivets. Screw are better because there is an possibility of xchange. These screww usually have freeskates, aggressive and semi-race skates (where there is higher possibility of damage). Fitness skates have often rivets. Longevity and resitance of buckles often rise together with price.
Microbuckle - usually sport models. Advantage is accurate and firm tightening.
Autolock buckle - the most common buckle. Side lever is loosen, then buckle is put to the counterpart and then again lever is tighten.
Velcro - simple velcro which is either attached with rivet or it is directly sewn in. In some cases, it can be replaced by new due to metal loop.





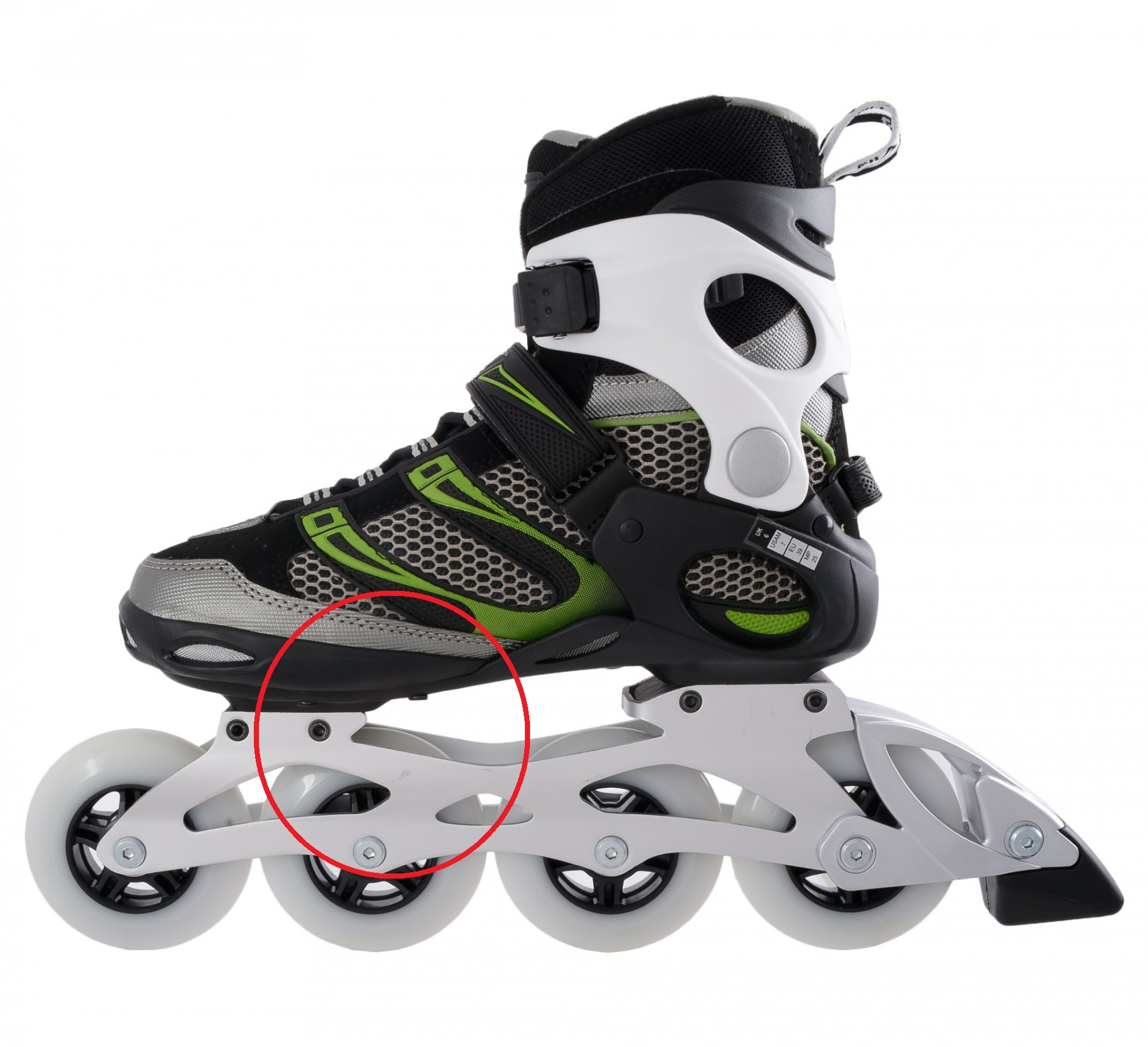
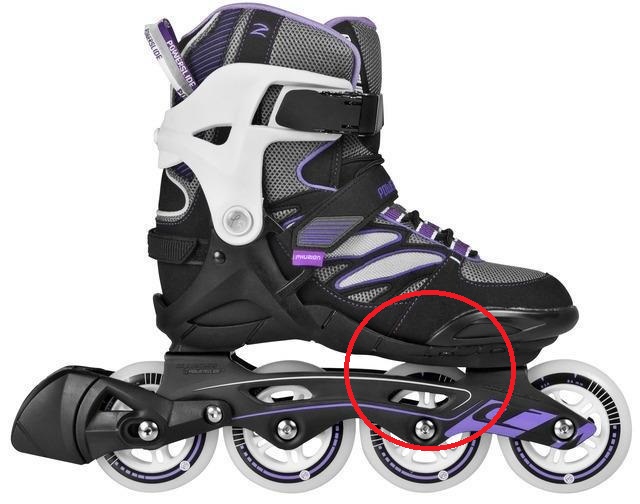
Focus point
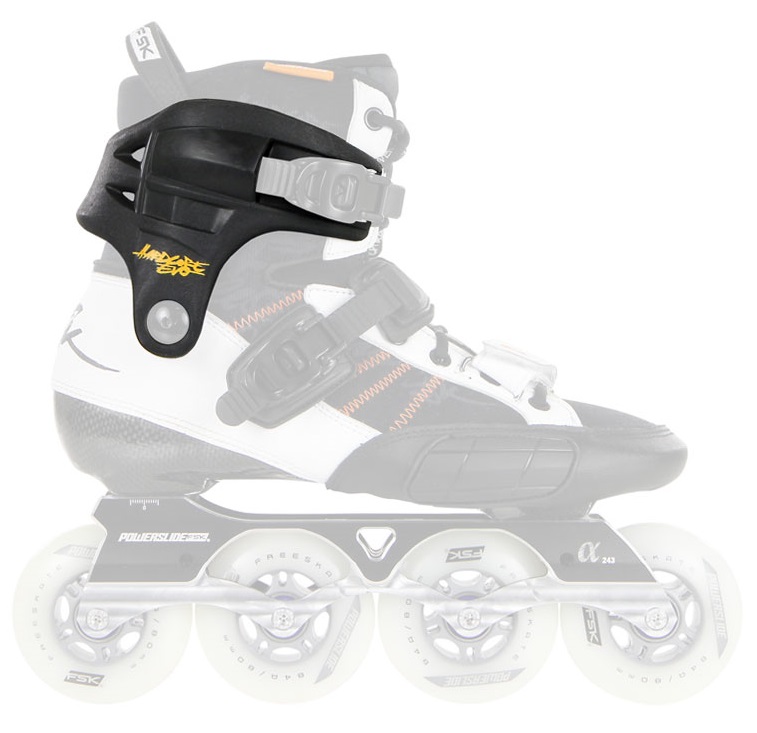
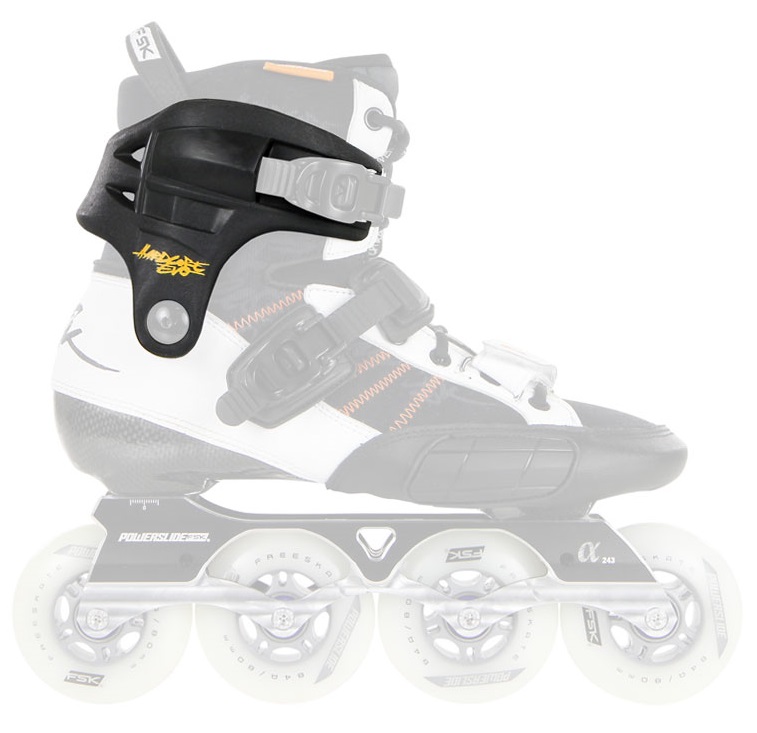
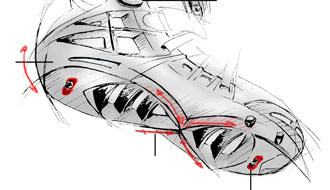
Position of focus point is very important for stability and controllability of skates. Unfortunately, it´s underestimated aspect. The most important is size of wheels - the bigger the wheels are, the higher the focus point is - which means worse stability and controllability. Position of focus point depends on the second wheel. You therefore can sometimes see that the second wheel si smaller than others (for nstance: 3x 100mm + 1x90mm). Or some skates have the bottom of the skate a bit grounded to lower the position of focus point.
Important is also quality of boot and frame. Minimum space between the second wheel and the boot is sign of quality. It provides the lowest possible focus point and thus good ratio of speed to stability. But this is a bit difficult to manufacture so mainly rather expensive skates have it. Focus point is very important when it comes to freeskates and speedskates. In case of 3wheel skates the focus point depends on the first wheel.
Example of unnecessarily high focus point, the space between the second wheel and the boot is too big (fila Matrix 90,picture. no. 1 and 2), on the contrary the third model has minimum space, better construcion provides lower focus and better stability (Powerslide Epsilon Pure, picture. 3). In case of 3wheel skates the focus point depends on the first wheel - the space between the first wheel and the frame should be minimal (picture 4).




Ventilation of boot
Usually it depends on used textil material or sometimes there are special holes for good air circulation. Ventilation is important more when it comes to fitness skates rather than speedskates. Direct ventilating holes are usually in area of tip or in the bottom of the boot. It is also matter of comfort, but always remember that feet sweat in skate - in some skates more, in others less. If you are concern about sweating, you can take into account vents. But most of the skaters are interested in the shape of skate and quality, ventilation is usually just pleasing bonus.


Weight
 It is parameter that is more imporant for professional speedskaters, slalom racers and long track enthusiasts. But more and more fitness skaters also take weight into consideration. Sometimes there is lightweight skate released who is considered to be the lightes in the world. For instance ultralight Powerslife Vi Flyte. The skate weights aprox. 1200g, but this means that the skate is more fragile. Also the maxi. capacity is lower and shorter lifespan of wheels (there is less PU substance in them in order tu cut down the weight even more)
It is parameter that is more imporant for professional speedskaters, slalom racers and long track enthusiasts. But more and more fitness skaters also take weight into consideration. Sometimes there is lightweight skate released who is considered to be the lightes in the world. For instance ultralight Powerslife Vi Flyte. The skate weights aprox. 1200g, but this means that the skate is more fragile. Also the maxi. capacity is lower and shorter lifespan of wheels (there is less PU substance in them in order tu cut down the weight even more)
Generally it can be said that regular skater won´t recognize difference if the skate weights several grams more. On the other hand, if your skate weight 1800 or 1200 grams, you will recognize it during acceleration, sprints and longer tracks. Someone can prefer solid heavy boot which would be more resistant and demanding for ride.
Weight depends mostly on material of the shell and frame (carbon, plastic, composite, aluminium, magnesium), technical manufacturing (removable inner insole, attachement of the frame and shell, skeleton, tughness of the frame etc..). Also significant weight have wheels - here depenends on size.
Cuff height/ front-back flex
Height of chimney (cuff) and front-back flex is determined by particular skating posture. Generally, the sporty posture, the lower cuff and softer front-back flex is required. It is because that sport posture pressure more on knees and shoulders are forward. The more you skate in such position, the lower skate your need (or at least softer flex). For t his reason are the racing skates low. Low boot enables to learn correct racing technique (outer curve, double push, etc.). Notice that the bigger the wheels, the lower the cuff. At the same time don´t be afraid of soft front-back flex (= mobility of the cuff in boot joint forward and backward), it is important. The purpose of cuff is to support ankle from the side.
Different needs are connected with freestyle and aggressive skates where the skate has to offer support for tricks.




Availability of spare parts
Availability of spare parts is common problem, mostly with unknown chain producers but also some other producers. The most common issue is with brake which is worn out quickly and spare brake is not available (brake is usually different for particular skates). Another problem is with atypical screws.
Solution is to buy skates in specialized shops and find information about spare parts before the purchase.
We have many of spare parts available in our shop and as an authorized store we are able to provide all spare parts for skates (from producers and brands we sell and which are available in Czech market)
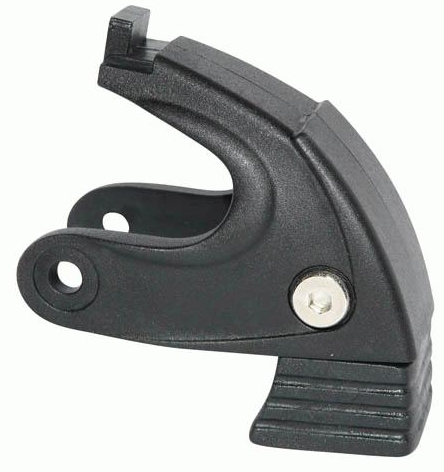




Details (material and quality of screws, precise sewing, shape of insole, absorbing, type of brake, type of spacers etc.)
In this chapter we are going to describe the most common technical details of skates. They don´t significantly affect quality of skate and skating, but it is better to know about them.
Construction - shell a cuff
they are common expressions for boot skeleton - the solid part which the textil part is attached to. Usually there are two parts - upper part (cuff) which is part from ankle upwards, from ankle downwards it is shell. Both parts are attached with rivet or screw.
Manufacturins, material and toughness of this construction have significant effect on overall quality of skates!
Shell - bottom part of plastic construction (textile boot) or the whole part of boot (composite or plastic boot) from from ankle downwards.
Cuff - upper, usually plastic cuff which connects chimney of the skates from ankle upwards.

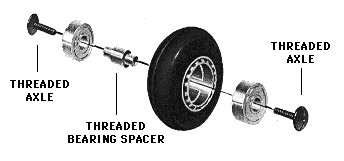
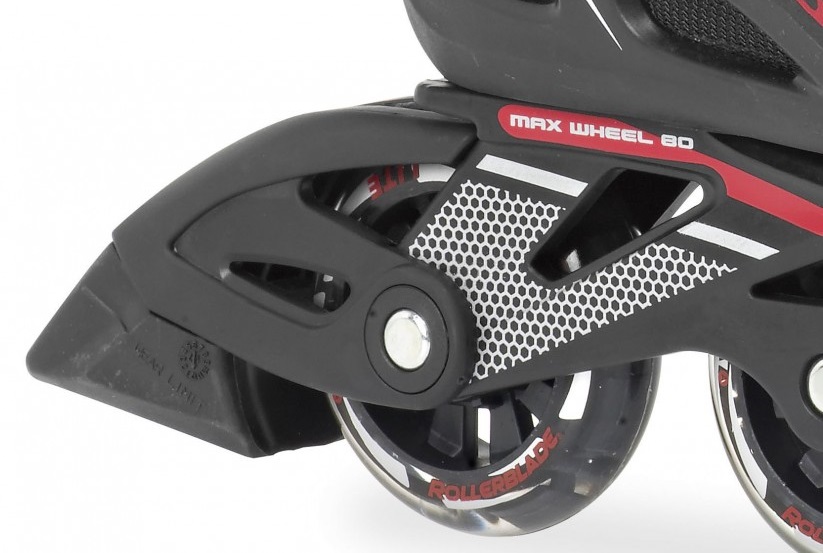
screws
screw hold wheels in the frame and they differ in material and shape. Quality can be also expressed by resistance against the tear, weight or lifespan. Longer screw is used for skates with brake (just for the certain wheel).
There are 6 and 8 mm screws. Then screw are divided according to type:
singel axels - for speed skates and one-piece frames (speed, freestyle). These axels have thread and they are directly screwed into the frame (where is thread). Advantage are lower weight and possibility of removing with just one wrench. The size is always 8mm. The thread can be different ( M6,M7), also material (lightweight aluminium, hardened aluminium), head (socket, torx) or conic rise of the head.
traditional screw with counterpart - classic screw, usually used with allen key. They are put into the frame against each other or they are shaped specially so they fit into the frame precisely (K2, Rollerblade), so they can be tightened with just one key.






Shocabsorber
Some skates have schockabsorber - a rubber or polyurethan pad providing absorbing of bumps. It is either part of boot or part of insole. Usually it is placed under the heel, sometimes also under the tip. It is mainly used in freestyle and aggressive disciplines in order to absorb jumps. Comfortable ride is provided by it when it comes to fitness skating.
Shockabsorbers can be bought separately for comfort improvement. You can find them in section tuning.




Brake
Typical skate placed under the heel is used only with kids and fitness skates. Trek and terrain skates have special brake. All other types of skates don´t have brake (freeskate, speed, aggressive, semi-race). It is expected that skaters are experienced and can brake quicly and efficiently without the brake.
Brake can be shift from one skate to another (right to left). Some producers have standardized shape of brake block. Others have various of brakes for certain types of skates. Lifespan is different and it is connected with price or certain brand. Brake is common spare part and you should check up on its availability. There is universal brake however it cannot be used with all skates.
Advantage of brake is relatively qucik and efficient braking. Disadvantage is that it is sometimes obstructing part. Additionally, once the skater learn how to brake using various combination (pluh, bogna, powerslide, T, curves), he does not want ordinary brake anymore. Brake is therefore most used by recreational and fitness skaters. If you are interested in skating tricks (bogns, shuffle, reverse ride etc.) we recommend to dismount the brake.





Liner (removable inner liner)
Some skates have removable inner liner just like skiboots have. Typical example are hardshell boots with solid plastic skeleton, but some fitness skates have this option as well. Quality of liner differes in price. Expensive liners have significantly better shape and material which provides higher comfort. Also firmness of padding can differ, sport skates have thinner liner made of dense foams which provides precise and efficient energy transform. Top levels have heat mouldable liners.
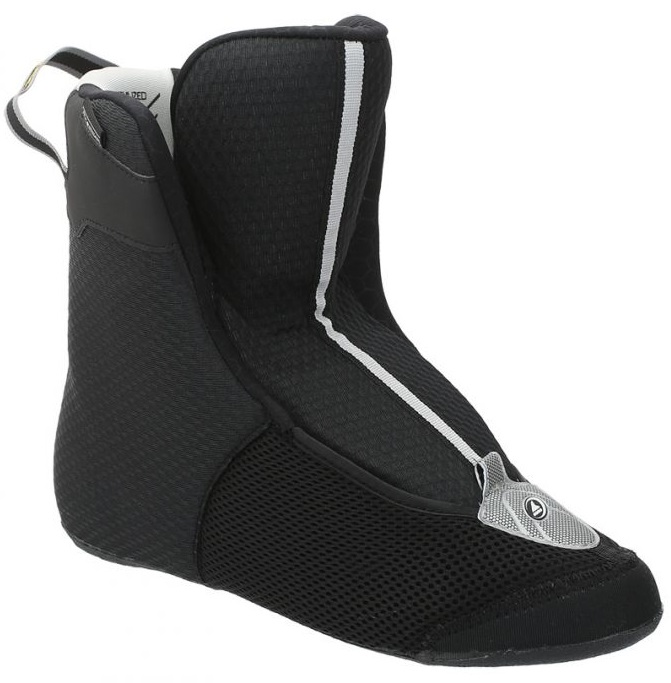




ano, jedná se o liner a najdete jej např. zde:
https://www.koleckove-brusle-praha.cz/vlozka-liner-do-sklet-brusli/
U lepších linerů počítejte s cenou kolem 1 500 Kč a mají zpravidla funkci tepelného tvarování.
V případě dotazů bude nejlepší probrat vše telefonicky - 725 544 060
S pozdravem
Strnad Lukáš
Inline Centrum